Low Visibility Operations Masterclass | Part 1
Understanding the Critical Procedures and Training Behind LVOs
Hey everyone and welcome back to this A320 Knowledge Masterclass.
In this article, we’ll dive into the world of Low Visibility Operations (LVO), exploring why these procedures are essential, how they work, and the rigorous standards that ensure they are performed safely. From the statistics behind LVO-related incidents to the training pilots undergo, we will uncover the complex, safety-driven framework that supports aviation operations under challenging visibility conditions.
Let’s dive right in.
Insights at a Glance:
Low visibility is a leading contributor to aviation incidents, particularly for commuter and air taxi operators.
Specialized LVO procedures help ensure safety and efficiency, particularly when visibility drops below 550 meters.
Both the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) and regional bodies like the FAA and EASA set the standards for LVO procedures.
Strict training requirements and certification ensure that pilots and airports are prepared to handle low visibility conditions.
Subscribe to the A320 Knowledge YouTube Channel!
Understanding the Importance of Low Visibility Operations
Low visibility and poor weather conditions pose significant safety risks in aviation. According to the US National Transportation Safety Board, reduced visibility is a factor in 37% of incidents involving commuter and air taxi operators. Under these circumstances, accidents often happen when pilots lack the necessary qualifications or experience, leading to severe outcomes such as loss of control, Controlled Flight Into Terrain (CFIT), runway incursions, or ground collisions.
However, commercial airlines, whose pilots are extensively trained in Low Visibility Operations (LVO), experience significantly fewer accidents in such conditions. This training helps ensure that pilots are well-prepared to handle reduced visibility safely, reducing the risk of serious incidents.
While safety is the primary focus of LVO protocols, low visibility also has a considerable impact on operational efficiency. Reduced visibility decreases airport capacity, complicates flight schedules, and creates logistical challenges for air traffic control teams. In this context, LVO procedures not only mitigate safety risks but also enhance operational flow during adverse weather conditions.
What Exactly Are LVO Procedures?
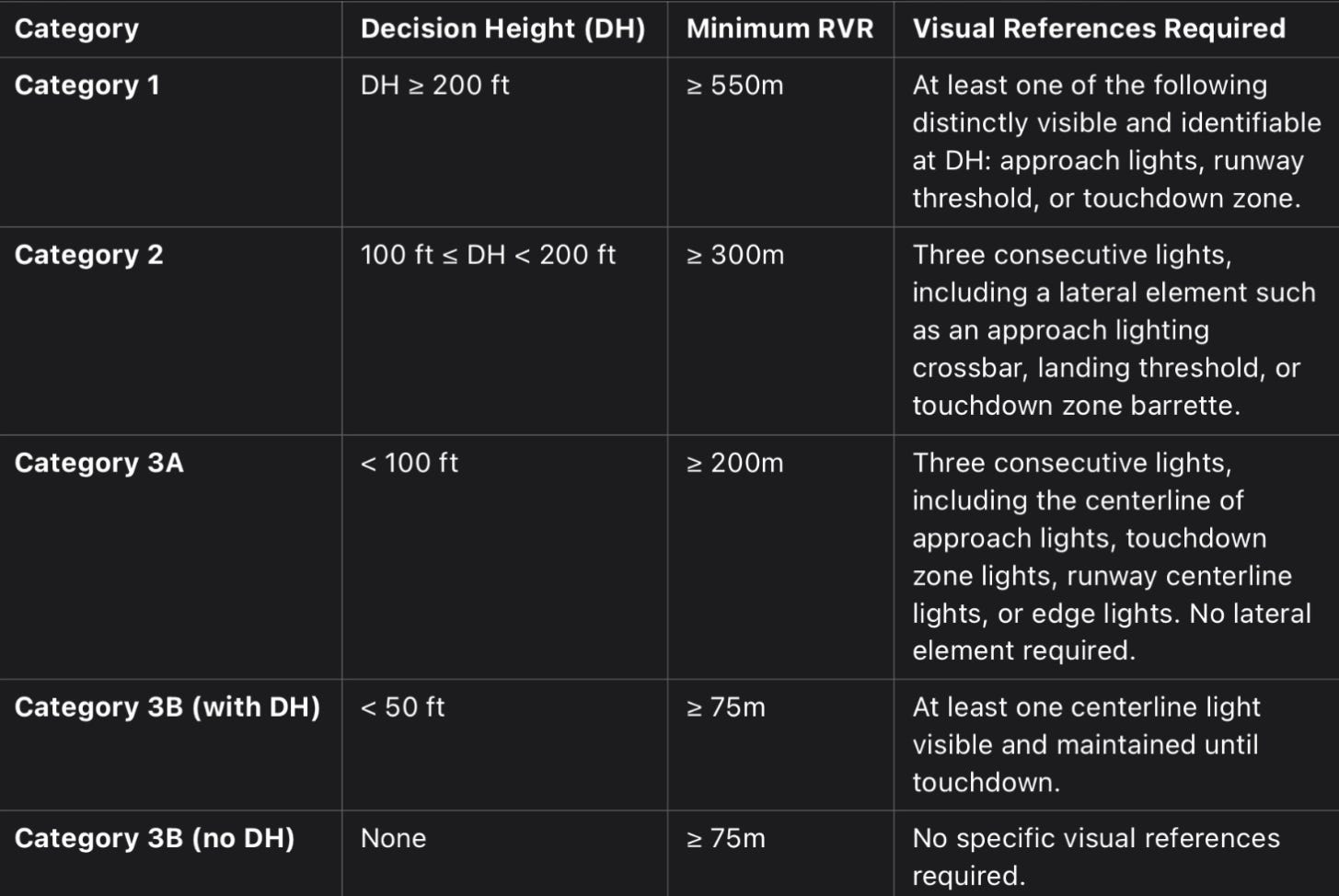
LVO procedures are a set of specialized protocols that are implemented to ensure that flights can operate safely when visibility is poor. These procedures become particularly critical when Runway Visual Range (RVR)—the distance over which a pilot can see the runway surface—drops below 550 meters, which typically occurs during fog, snow, or heavy rain.
LVO procedures are used to facilitate operations under Category 2 (Cat 2) and Category 3 (Cat 3) conditions. These categories represent different levels of visibility restrictions and have specific requirements for both pilots and airports:
Category 2 (Cat 2): Operations are allowed when RVR is between 300 meters and 550 meters. Aircraft and crews must meet specific equipment and training requirements.
Category 3 (Cat 3): This is for the most challenging conditions, with RVR dropping below 300 meters. Cat 3 procedures are highly specialized and require advanced technology and rigorous training for flight crews.
In addition to these requirements, the airport itself must have specific infrastructure in place, such as high-precision instrument landing systems (ILS), runway lighting, and other equipment designed to assist pilots during low visibility conditions.
The Global Standards: ICAO, EASA, and FAA
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) plays a pivotal role in setting the global framework for aviation safety, including standards for Low Visibility Operations. ICAO’s guidelines are adapted regionally by governing bodies like the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
ICAO: The global authority for aviation standards, ICAO sets the foundational requirements for LVO procedures. These guidelines ensure consistency and safety in operations worldwide. ICAO's standards address everything from the equipment needed to the specific training requirements for pilots and air traffic controllers.
EASA: In European airspace, the EASA outlines the regulations that airlines and airports must adhere to when operating under low visibility conditions. These regulations ensure that LVO procedures are carried out consistently across European nations, maintaining high safety standards.
FAA: Similarly, the FAA in the United States has developed its own set of regulations and guidelines. The FAA’s regulations on LVO are codified in the Code of Federal Regulations and provide detailed instructions for airports, airlines, and pilots. These regulations cover everything from runway markings to the certification of aircraft and flight crews for Category 2 and Category 3 operations.
By aligning international and regional standards, ICAO, EASA, and the FAA help ensure that low visibility conditions are managed safely and efficiently worldwide.
How LVO Procedures Impact Airline Operations
Low visibility significantly impacts airline operations, leading to delays, slower taxi speeds, and reduced capacity for arrivals and departures. In such conditions, air traffic controllers must manage traffic more carefully, spacing aircraft further apart to maintain safe separation. The need for deicing, which may be required during precipitation, adds another layer of complexity to operations.
Despite these challenges, LVO procedures help mitigate the risks posed by low visibility. By following strict protocols, pilots are able to safely navigate these conditions and maintain control of the aircraft. Air traffic controllers also play a crucial role, adjusting flight schedules and guiding aircraft through low-visibility airspace with heightened precision.
Without the implementation of LVO protocols, the risks of incidents such as runway incursions or ground collisions increase significantly. By following established LVO procedures, however, airports and airlines are able to ensure that operations continue smoothly even in challenging weather conditions.
Pilot Training for Low Visibility Operations
A key aspect of LVO is the specialized training required for pilots before they are certified to conduct Category 2 or Category 3 operations. This training is a multi-faceted process that ensures pilots are well-prepared to handle the complexities of low-visibility flying.
Ground Theory Courses: Pilots must first undergo in-depth theoretical training, which covers the technical aspects of LVO, including the equipment used, the specific regulations in place, and the strategies for managing low-visibility conditions.
Simulator-Based Training: After completing the theoretical portion, pilots undergo practical training using flight simulators. These simulators replicate real-world low-visibility scenarios, giving pilots hands-on experience without the risk of actual flight.
Computer-Based Programs: Many airlines use computer-based training programs to supplement theoretical learning. These programs provide interactive lessons and scenarios, ensuring that pilots can reinforce their knowledge and skills in a flexible, self-paced environment.
Certification: Only after completing both the ground theory and simulator-based training can pilots be certified to operate under Category 2 or Category 3 conditions. This certification ensures that pilots have the necessary knowledge and experience to navigate low visibility safely.
Conclusion: Ensuring Safety and Efficiency in Low Visibility
Low Visibility Operations (LVO) are a critical aspect of modern aviation, ensuring that flights can continue safely and efficiently even when visibility is severely restricted. By adhering to rigorous protocols and training standards, airlines, airports, and pilots work together to reduce the risks of accidents, such as runway incursions or controlled flight into terrain, that could arise in such conditions.
While LVO procedures add a layer of complexity to operations, they are essential for maintaining safety in adverse weather conditions. As aviation technology advances and weather patterns continue to shift, the importance of LVO will only grow, making it more vital than ever for pilots and airports to remain prepared for low visibility scenarios.
Key Takeaways:
Low visibility contributes to a significant portion of aviation accidents, especially for commuter and air taxi operators, but commercial airlines with specialized training experience fewer incidents.
LVO procedures, including Category 2 and Category 3 operations, are critical for ensuring safe flights under low visibility conditions.
ICAO, EASA, and FAA regulations provide a global framework for LVO procedures, ensuring consistency and safety across regions.
Specialized pilot training, including ground theory, simulator exercises, and certification, ensures that flight crews are fully prepared to operate safely in low-visibility conditions.
If you found this Masterclass helpful, consider sharing it with others or leaving a comment below with your thoughts.
I’ll see you in the next one.
A320 Knowledge